Design and Construction Transition Guidelines for Concrete
requirement for the design of a pavement transition for a variety of pavement types and terminal configurations that suitable for use 17 Key Words Concrete Pavement, Transition Area, Design, Construction, Guideline, Joint 18 Distribution Statement No Restrictions This document is available to the public through NTIS: National Technical Concrete pavement transition elements may involve only a single joint and a single slab panel, a series of joints and slab panels, or short sections of adjoining pavements Improperly designed pavement transition elements lead to poor pavement performance and the need for frequent maintenance and repairBest Practices of Concrete Pavement Transition Design and This transition should be smooth as well, avoiding dangerous trip hazards Concrete transitions onto the street: When it comes to the transition from the street onto the asphalt, just like the garage, the subgrade should be excavated down equivalent to the thickness of concrete that’s being installed This transition should be smooth as wellConcrete Transitions All About DrivewaysAsphalt driveways are a great alternative to concrete driveways when it comes to cost and a great alternative when it comes to gravel driveways when it comes to a solid surface But when installing a new asphalt driveway, the transitions, meaning where the asphalt meets the garage floor, sidewalks and the street should be a smooth transitionHow Are Transitions Into The Garage, Sidewalks If, when pouring the concrete right up against the asphalt, you end up with parts of the concrete that taper or feather out to less than say about 15 > 20 inches thick you will have trouble keeping the concrete in one piece The thin parts are likely to fracture and break offpouring concrete right next to asphalt driveway

Pavement Tapers and Transition Guide
Pavement Tapers and Transition Guide December 31, 2008 Abstract: The following information is being provided as guidance to assist Design Engineers in designing pavement transition tapers The transition tapers presented in this guide meet the Caltrans standards and requirements for pavement transition tapers01011990 You won't be able to transfer load directly from a concrete slab to a flexible pavement If you're stuck with an asphalt parking lot, the best approach is to pave a concrete apron around the building, with a slope that will ensure adequate drainage away from the building Thoroughly compact the subgrade and base material adjacent to the apron, and slope the asphalt Joint Detail Where Asphalt Pavement Meets a TYPICAL TRANSITION BETWEEN CONCRETE AND FLEXIBLE PAVEMENTS \ 1500 rn 19>t lilling PVC anti corrosive sleeve 2000 B A REF Ceogrid • nole 2 odded Description 01 sleeve revised Former og No H1005A with general revision REVISION Nov 96 Sepl96 llne 94 SICNATUR DATE HIGHWA YS DEPARTMENT REFERENCE DRAWING No I CAD SCALE Typical Transition betweeb Concrete and Flexible PavementsEasy tutorial showing how I make paved roadsHowTo Tutorial Pavement and/or Asphalt for Slope the vertical face of the concrete transition at about 2030 degrees This allows the asphalt interface to always be pushed against the concrete, thus more likely maintaining a closed joint between the two It also provides additional support to the asphalt pavement at a high stress areaAsphalt pavement to concrete slab continuous

Concrete Transitions All About Driveways
This transition should be smooth as well, avoiding dangerous trip hazards Concrete transitions onto the street: When it comes to the transition from the street onto the asphalt, just like the garage, the subgrade should be excavated down equivalent to the thickness of concrete that’s being installed This transition RE: Concrete/Asphalt Transition civilman72 (Civil/Environmental) 20 Oct 14 11:59 Make sure the final elevation of the asphalt is constructed a bit higher (~1/4") than the concreteConcrete/Asphalt Transition If, when pouring the concrete right up against the asphalt, you end up with parts of the concrete that taper or feather out to less than say about 15 > 20 inches thick you will have trouble keeping the concrete in one piece The thin parts are likely to fracture and break offpouring concrete right next to asphalt driveway The primary motivation behind this project was to design a transition from a freestanding Fshape temporary concrete barrier to the pinneddown temporary concrete barrier developed by TTI This first phase had the objective of determining if there is an equivalency between an anchoring pin installed in concrete pavement and a pin installed in some thickness of asphalt pavementTransition for Anchored Temporary Concrete severe pavement transitionconcrete to asphalt at 448482 W 3300 S Salt Lake City, UT, 84115, USA: west bound lanes hit a 2 to 3 inch bump at concrete to asphalt transition severe impact Needs to be planed down height varies by season This has been there for years it is very hard on your alignment and suspension It is like hitting a deep potholesevere pavement transitionconcrete to

The Complete 7Step Process for Asphalt
Step 7: Butt Joints and Transitions It is very rare to install an asphalt surface that does not connect to existing driveways, roadways or parking lots As such, asphaltpaving contractors must find a way to smooth the transition from old surface to new Butt joints are areas where old asphalt or concrete meets new asphalt pavement Asphalt Concrete Pavement transition and approach road paving For projects where transition ACP is required, the Contractor shall cold mill to achieve a 40 mm minimum thickness of ACP The joint between the existing ACP and the new transition ACP shall be sawcut a minimum of 40 mm across the full width of roadway Milling shall be considered asSECTION 17 ASPHALT CONCRETE PAVEMENT Albertaca02102003 An asphalt or concrete pavement may be milled to remove distressed layers or material, make crown corrections, maintain curb heights or vertical clearances, scarify existing surfaces, profile existing surfaces, remove asphalt overlays, or provide pavement transitions in accordance with Recurring Special Provision 306R463, attached heretoINDIANA DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATIONRMS R101:Cold Milling of Road Pavement Materials RMS R83: Concrete Pavement Base RMS R82: LeanMix Concrete Subbase (b)All asphalt pavement dimensions relate to compacted asphalt (a)All dimensions are in millimetres unless noted otherwise; 3 Dimensions: and constructors 2 These Drawings provide standard details for use by both designersAsphalt drawings Volume 1 New Construction31032020 Asphalt Driveway Cons Shorter lifespan – Asphalt doesn’t last as longThe lifespan is generally about 15 to 20 years – half that of concrete More maintenance required – Asphalt needs to be resealed every three to five years, particularly if you want it to last; Oily texture – Asphalt has an oily texture that softens in heat or direct sunlightAsphalt Driveway Cost vs Concrete Driveway

Understanding the Guide to Concrete Overlays of Asphalt
Guide to Concrete Overlays of Asphalt Parking Lots 1 Construction Details Best Practices 8 Transition Details and Blending New Construction with Overlay 9 Placement of Concrete and Equipment 10Fibers in Concrete Overlays 18 Zoned Parking Lot Design Areas • More Concrete Pavement professional development: Pervious ConcreteSmooth transitions are necessary to ensure the desired ride for the traveling public Transitions are used within projects as new pavement approaches a bridge to avoid adding unnecessary dead load on the bridge As roadways pass beneath bridges, transitions are used to avoid encroaching on the existing vertical clearanceNew Approach for Developing an Asphalt Bonded Concrete Overlays of Asphalt Pavements (BCOA) 2 1 Introduction Bonded concrete overlays of asphalt (BCOA) pavements are typically between 3 to 6 inches thick The bond between the asphalt and the concrete is critical to ensure that that the pavement behaves as one structure, especially for very thin concrete overlays This monolithic Guidelines for Bonded Concrete Overlays of Asphalt The primary motivation behind this project was to design a transition from a freestanding Fshape temporary concrete barrier to the pinneddown temporary concrete barrier developed by TTI This first phase had the objective of determining if there is an equivalency between an anchoring pin installed in concrete pavement and a pin installed in some thickness of asphalt pavementTransition for Anchored Temporary Concrete 1) Projects where asphalt concrete is only used to transition pavement or structure modification or replacement to existing pavement Medium Traffic project: Use a 448 Type 1 surface course with PG 6422 for surface and intermediate courses of asphalt concrete and a 301 or 302 with PG 6422 for a base coursePAVEMENT GUIDELINES FOR SMALL QUANTITY ASPHALT CONCRETE

Road Pavement Design Guide Kent County Council
b) the surfacing layer is to be concrete or clay pavers, setts or flags/slabs c) traffic requirements mean that more than 180 mm of asphalt overlay is required ie a Total Design flow in excess of 20msa A pavement construction may need to satisfy 4 structural functions:23 ASPHALT CONCRETE PAVEMENT A Asphalt concrete paving shall be Type IIIC2PG 6410 conforming to SSPWC Section 203 24 FOG SEAL COAT A Seal coat shall be SS1h asphalt emulsion conforming to SSPWC Section 2033 PART 3 – EXECUTION 31 SUBGRADE PREPARATION A Scarify 6 inches below new pavement section, bring to optimum moisture 02743 ASPHALT CONCRETE PAVEMENTOverlays (either structural or nonstructural) make up a large portion of the roadway paving done todayThe degree of surface preparation for an overlay is dependent on the condition and type of the existing pavement Generally, the existing pavement should be structurally sound, level, clean and capable of bonding to the overlayExisting Surface Preparation for Overlays Many years ago I designed a transition between asphalt and concrete that has served well The concrete face at the interface between asphalt and concrete is sloped so that when traffic goes from asphalt to concrete, it actually pushes that asphalt harder against the concrete, thus helping to maintain the seal Attached is a detail of this conceptRepair asphalt with concrete patch 31032020 Asphalt Driveway Cons Shorter lifespan – Asphalt doesn’t last as longThe lifespan is generally about 15 to 20 years – half that of concrete More maintenance required – Asphalt needs to be resealed every three to five years, particularly if you want it to last; Oily texture – Asphalt has an oily texture that softens in heat or direct sunlightAsphalt Driveway Cost vs Concrete Driveway
- bentonite solution hematite density
- Haiwang Stone Crusher Machine Crusher Plant For Mine
- Mud Rehandle Methode For Coal Mining
- Por le Rock Crusher Chassis Jaw Cone
- good quality small ball mill for sale
- Jaw And Gyratory Crushers, The Comparison Between Gyratory Crushers An
- Rock Crusher Ball Mills
- Wet Grinding Plants For Mica Scrap
- Minerals Crusher Mills In Delhi
- Chancadora Agregados Venta
- River Pebble Processing Equipment Manufacturer
- Small Gravity Gold Mill Flowsheet
- impactor crusher manufacturer
- Chinese Simple Operation Calcite Raymond Mill For Sale Is Disunt
- Stone Crusher Plant Job In Jamnagar
- gold grinding machinery
- grinding ating carbonate
- grinding process flexibility
- hopper crusher units in uae
- spare part for ne crusher hp 200
- clay crusher production industry
- sand ne crusher manufacturers india
- Open Pit Crushing Coal Mining Crusher
- crushing plant definitely
- mining semi mobile crusher china
- Laboratory Scale Ceramic Ball Mill
- Machinery Required To Manufacture Of Vermiculite In Chile
- metal metal crushing machine for sale
- Minerio De Ferro Peneiramento Maquina De Processamento
- invitation letter to seminar
- Pengolahan Ban Bekas Recycling
- grinder of abs product
- Buy Gravel Hauling Business Calgary
- faiv faiv roler grendr mill
- Albite Roller Crusher For Sale
- automatic type ne crushing plant india
- Limestone Grinding Affecting
- quartz grit making machine
- alloy steel for parts crusher crusheraggregate processing
- belt nveyor advancements
Stationary Crusher
Sand making equipment
Grinding Mill
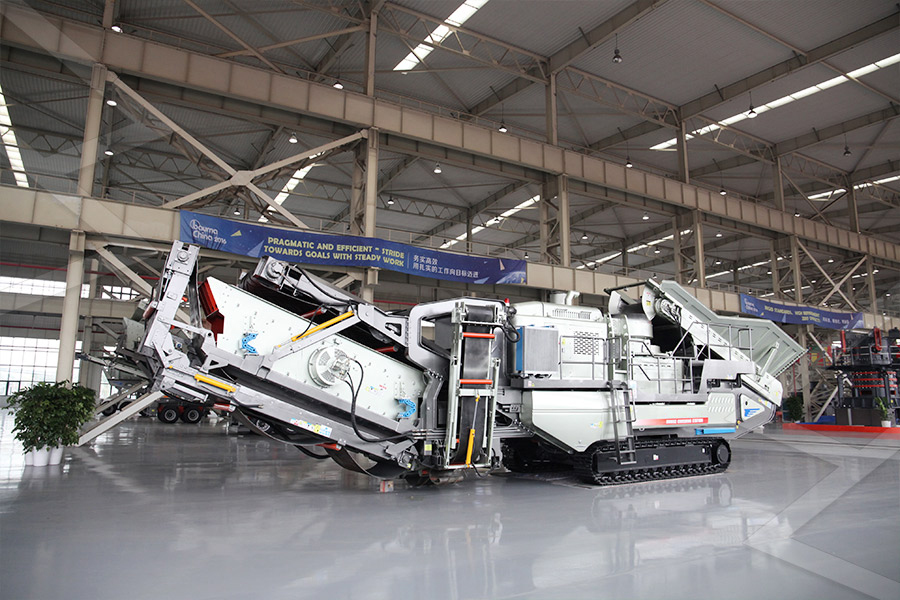
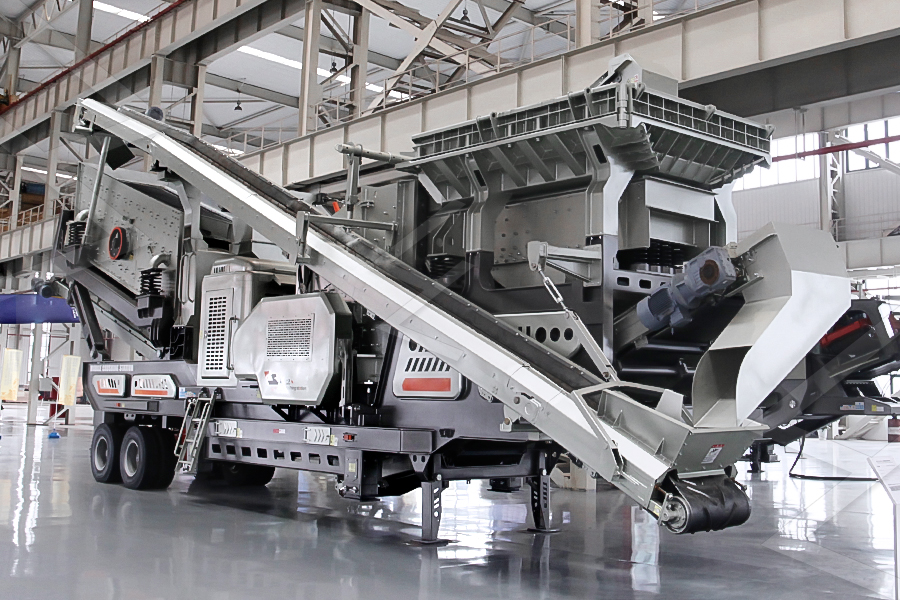
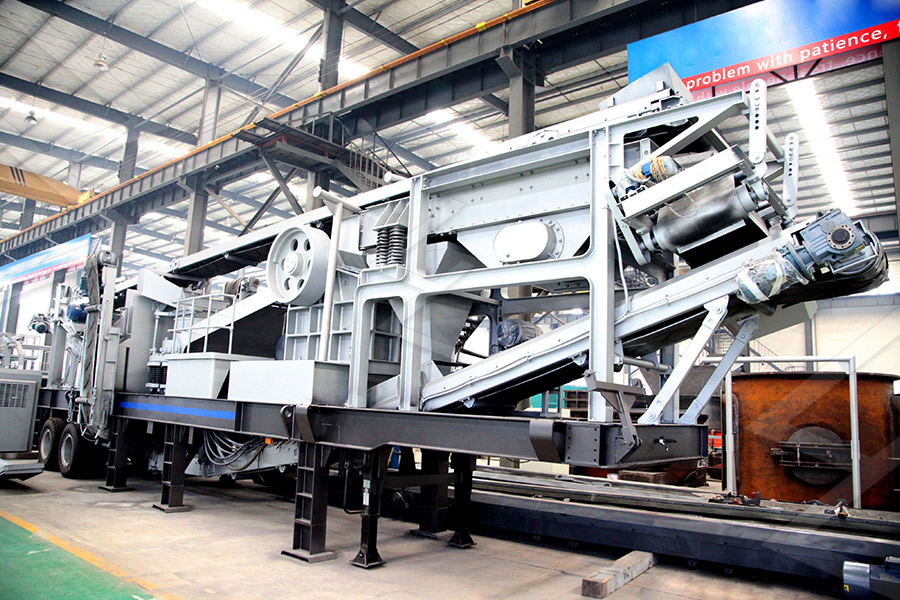
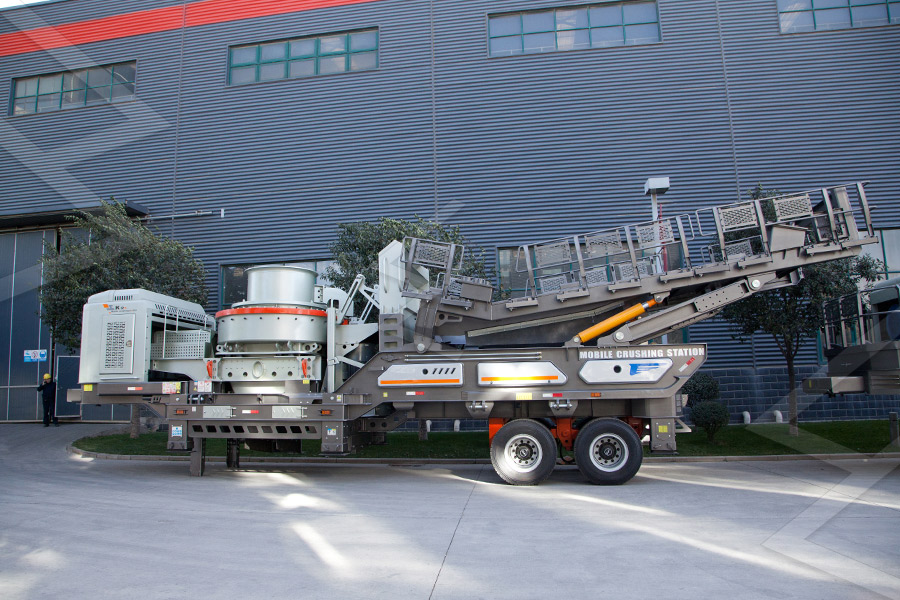
Mobile Crusher