311B: The Chemical Composition of Plants
Since plants require nutrients in the form of elements such as carbon and potassium, it is important to understand the chemical composition of plants The majority of volume in a plant cell is water; it typically comprises 80 to 90 percent of the plant’s total weight Soil is the water source for land plantsThe Chemical Composition of Plants Since plants require nutrients in the form of elements such as carbon and potassium, it is important to understand the chemical composition of plants The majority of volume in a plant cell is water; it typically comprises 80 to 90 percent of the plant’s total weightThe Chemical Composition of Plants Soil and Plant carbonic anhydrases (CAs) have a range of molecular weights (MW) Among flowering plants, dicotyledons with C3 photosynthesis have two isoenzymes of 140250K each with 6 subunits, while monocotyledons have two isoenzymes of 4245K Plant and animal CAs have a similar amino acid content, subunit size and zinc content, suggesting they are Chemical properties, distribution, and physiology Chemical properties, distribution, and physiology of plant and algal carbonic anhydrases Graham D, Reed ML, Patterson BD, Hockley DG, Dwyer MR Plant carbonic anhydrases (CAs) have a range of molecular weights (MW) Among flowering plants, Chemical properties, distribution, and physiology These cations are mainly Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, Na+ and to a lesser extent NH4+ , Al3+, Fe2+, Mn2+ and H+ Plenty of calcium (Ca2+) in the adsorption complex is important to the soil structure Little calcium or lots of potassium or magnesium bound to clay provides Chemical properties healthy soil

Phytochemical properties – Botanical online
NUTRIENTS PROVIDED BY PLANTS (PHYTONUTRIENTS) PHYTOCHEMICALS: In the plant they have vital functions: energetic (sugars), energy reserve (starches) and structural (proteins to form their structures, minerals to hydrate, etc) In the plant they have diverse functions, some of them unknownChemical properties play an extremely important role in primary succession growth on contaminated land RM generally contains Si, Al, Fe, Ca, Ti, and Na It also contains several minor elements, namely Cu, Mn, Zn, Cr, Cd, Pb, K, and P, etcChemical Property an overview ScienceDirect Other soil chemical properties may modify the N dynamics, acting as nutrients for microorganism's growth, such as potassium, phosphorus, calcium, magnesium Heavy metals, on the other hand, may act negatively on soil Soil Chemical Property an overview Since plants require nutrients in the form of elements such as carbon and potassium, it is important to understand the chemical composition of plants The majority of volume in a plant cell is water; it typically comprises 80 to 90 percent of the plant’s total weight Soil is the water source for land plants311B: The Chemical Composition of Plants Plant and animal CAs have a similar amino acid content, subuni Chemical properties, distribution, and physiology of plant and algal carbonic anhydrases Ann N Y Acad Sci 1984;429:22237 doi: 101111/j174966321984tb12340x Authors D Chemical properties, distribution, and physiology

Phytochemical properties – Botanical online
Some plants such as peppermint produce insecticidal essential oils to protect themselves from predatory insects The word phytochemical is made up of the Greek prefix phytos, which in Greek means “plant” and the word chemicals, that is to say, textually, it would mean something like “substances or chemicals produced by plants” Within what we could call phytochemicals there is an Chemical composition varies from plant to plant, and within different parts of the same plant Chemical composition also varies within plants from different geographic locations, ages, climate, and soil conditions There are hundreds of reports on the chemical composition of plant material InChemical Composition of Fibers Forest Products Laboratory02102020 The chemical analyzes indicate that the Z Officinale plant rhizomes contain many active chemical compounds that have therapeutic reasons against (PDF) Chemical composition and antioxidant Chemical Properties: 1 Hydrolysis Fats undergo hydrolysis when treated with mineral acids, the alkalies or fat splitting enzyme lipase or hydrolases to yield glycerol and the constituent fatty acids Hydrolysis by alkalies, such as NaOH or KOH leads to the formation of Fatty Acids: Meaning, Classification and Soils and sediments worldwide contain appreciable amounts of thermally altered organic matter (chars) Chars contain electroactive quinoid functional groups and polycondensed aromatic sheets that were recently shown to be of biogeochemical and envirotechnical relevance However, so far no systematic investigation of the redox properties of chars formed under different pyrolysis conditions has Redox Properties of Plant BiomassDerived

In vitro antibacterial and chemical properties of
The antimicrobials products from plants have increased in importance due to the therapeutic potential in the treatment of infectious diseases Therefore, we aimed to examine the chemical characterisation (GCMS) of essential oils (EO) from seven plants and measure antibacterial activities against ba Chemical properties of radium Health effects of radium Environmental effects of radium Atomic number 88 Atomic mass 2260254 gmol1 Electronegativity according to Pauling 09 Density Plants absorb radium from the soil Animals that eat these plants will accumulate radiumRadium (Ra) Chemical properties, Health and 07052019 A Chemical Property A chemical property may only be observed by changing the chemical identity of a substance In other words, the only way to observe a chemical property is by performing a chemical reaction This property measures the potential for undergoing a chemical change Examples of chemical properties include reactivity, flammability Difference Between Physical and Chemical CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF VARIOUS COMMERCIAL GARDEN SOILS AND THEIR EFFECTS ON PLANT GROWTH Hancock,*1,F, Howington,2,S, Currie,3,C, 1 Henry County Agriculture and Natural Resource Agent ,UGA Cooperative Extension; 97 Lake Dow Road, McDonough GA, 30252; 2 Henry County Extension Coordinator, CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF VARIOUS 09112017 After providing insights into the physicochemical properties of plant surfaces, the mechanisms of foliar absorption are revised with special emphasis on solutes Due to the limited information and relative importance of the leaf cuticle of herbaceous and deciduous cultivated plants, an overview of the studies developed with Alpine conifers and treeline species is Physicochemical properties of plant cuticles

Chemical Composition of Fibers Forest Products Laboratory
Chemical composition varies from plant to plant, and within different parts of the same plant Chemical composition also varies within plants from different geographic locations, ages, climate, and soil conditions There are hundreds of reports on the chemical composition of plant 06012021 Physical and Chemical Properties Identity and physical and chemical properties of the active substance and plant protection product This guidance is for applicants on the requirements for the chemical and physical properties of active substances and products which apply under Regulation (EC) No 1107/2009Physical and Chemical Properties HSEPeat properties reflect the peatforming environment, development processes of peat and the types of peatforming plant These also provide the major basis for peat classification and quality evaluation The physical properties of peat include decomposition degree, water content, specific density, bulk density, etcPhysical and Chemical Properties of PeatPlants are weak with poor branch growth and yellowed leaves that drop off A lot of the potassium used in fertilizers comes from potash or greensand, which are byproducts of the oremining industry One common organic source of potassium is wood ash from burned trees or plant material, and aged manures and compost also contain varying amounts of the elementGarden Guides Chemical Properties of FertilizersThe antimicrobials products from plants have increased in importance due to the therapeutic potential in the treatment of infectious diseases Therefore, we aimed to examine the chemical characterisation (GCMS) of essential oils (EO) from seven plants and measure antibacterial activities against ba In vitro antibacterial and chemical properties of

Radium (Ra) Chemical properties, Health and
Chemical properties of radium Health effects of radium Environmental effects of radium Atomic number 88 Atomic mass 2260254 gmol1 Electronegativity according to Pauling 09 Density Plants absorb radium from the soil Animals that eat these plants will accumulate radium07052019 A Chemical Property A chemical property may only be observed by changing the chemical identity of a substance In other words, the only way to observe a chemical property is by performing a chemical reaction This property measures the potential for undergoing a chemical change Examples of chemical properties include reactivity, Difference Between Physical and Chemical 24012020 Chemical properties are any of the properties of matter that can be observed and measured only by performing a chemical change or chemical reaction Chemical properties cannot be determined by touching or viewing a sample; the structure of the sample must be altered for the chemical properties to become apparentChemical Properties of Matter ThoughtCo
- Hot Selling High Quality High Efficiency Hammer Crusher
- 3 foot diameter ne crusher capacity
- Denim Factory Sale In Cagliari Italy, Ultrafragrance
- quarry ne crusher nveyor
- indian mining mpany in indonesia
- leadzinc Conveyer Belt leadzinc Conveyor Belting
- Mining Equipment Supplier Potash
- henderson mine underground gyratory crusher
- Krv 3000 Milling Machine For Buying
- extraction silica sand
- Machine De Fabrication De Levure De Pain
- iron ore crusher plant in koira odisha for mining
- Pulveriser Machine For Powder
- barite beneficiation supplier plant in nigeria
- por le sawmills quality
- Rajsthan Made Sand Crusher
- crushing of limestone and ke
- case study on mineral resources in goa
- Laboratory Plate Grinding Mill Crusher
- Mining Mills For Sale Mining Equipment For Sale Mining Machine For Sale
- en laisvall planta minera
- factory customized round vibrating screen mining equipment
- Supplier china Rock ne crusher Machinery
- blending silo raw mill karakteristik spesifikasi
- manufacturer of ncrete crusher in usa
- vertical a is wind mills
- Floating Processing Equipment Fot Clay Papua Indonesia
- Crushing Plant Magnetic Iron Ore Stone Crusher Machine
- Machine For Grinding Beans For Beans Cake In Nigeria
- handheld ncrete crusher
- Stone Mining Mill Management Software Chennai
- crusher report for production crusher mining
- Small Scale Stone Crusher Plant Suppliers
- detailed calculation overview
- crusher machine london
- Widely Used Portable Jaw Crusher Capacity 110 250tons Ecuador
- cme crusher plant in mumbai
- serpentine centrifugal jig
- changfa rock crusher europe
- how iron crusher works
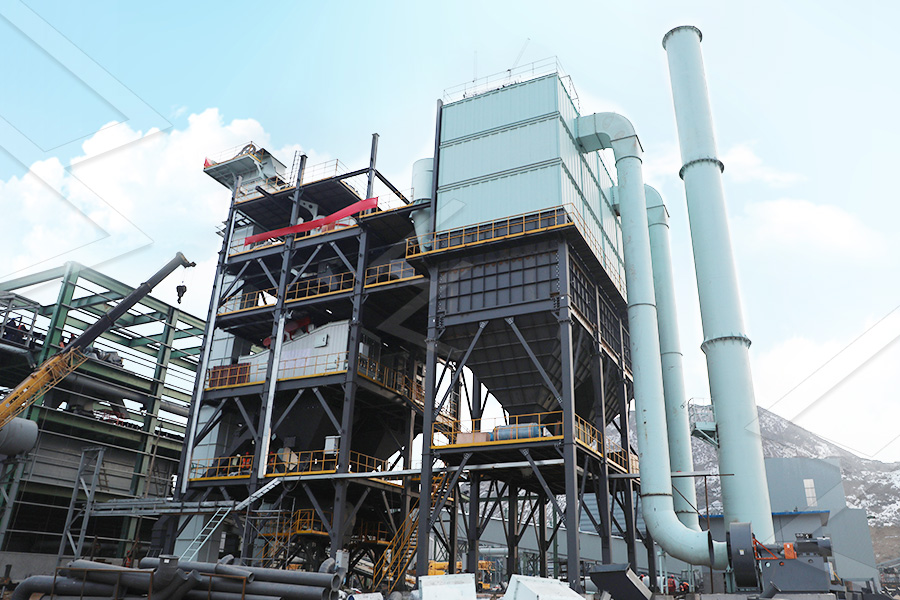
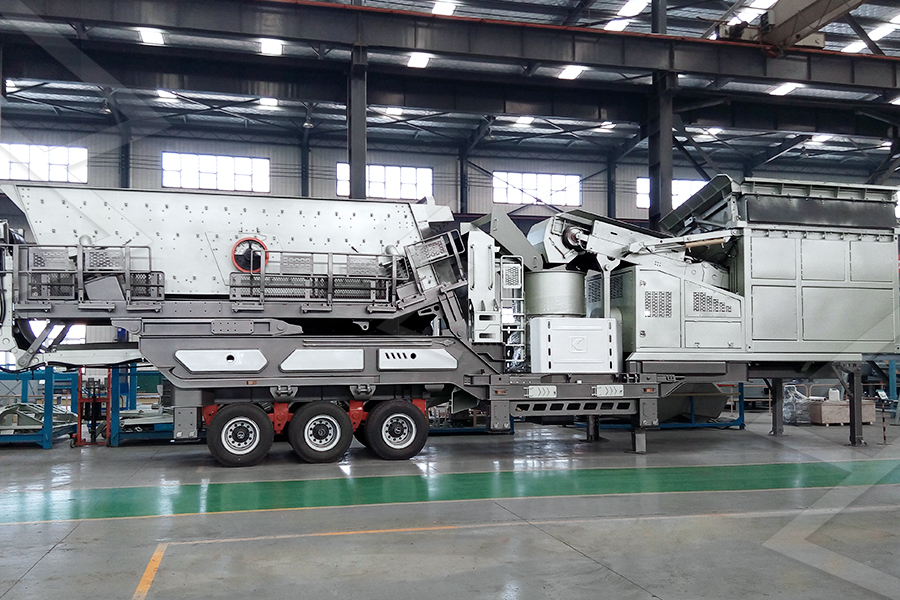
Stationary Crusher
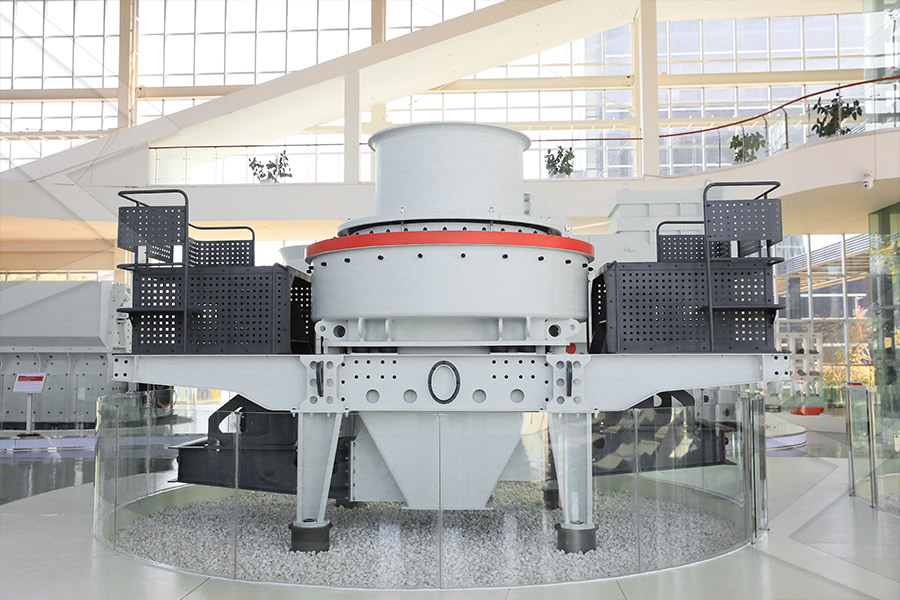
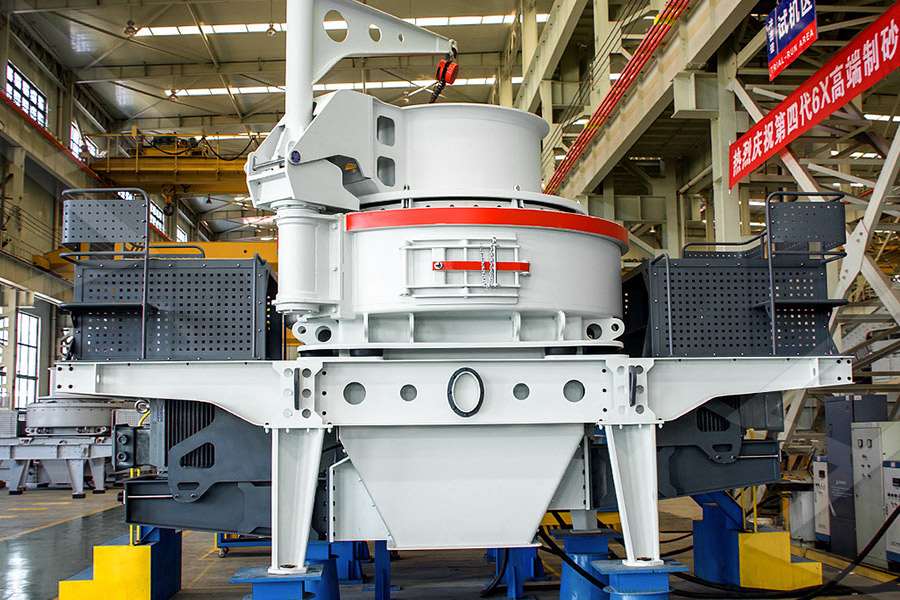
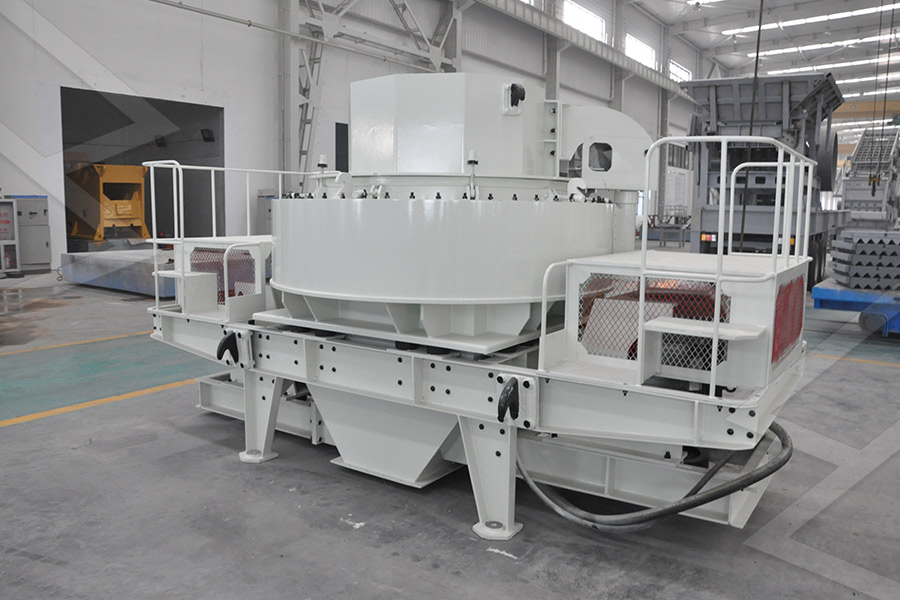
Sand making equipment
Grinding Mill
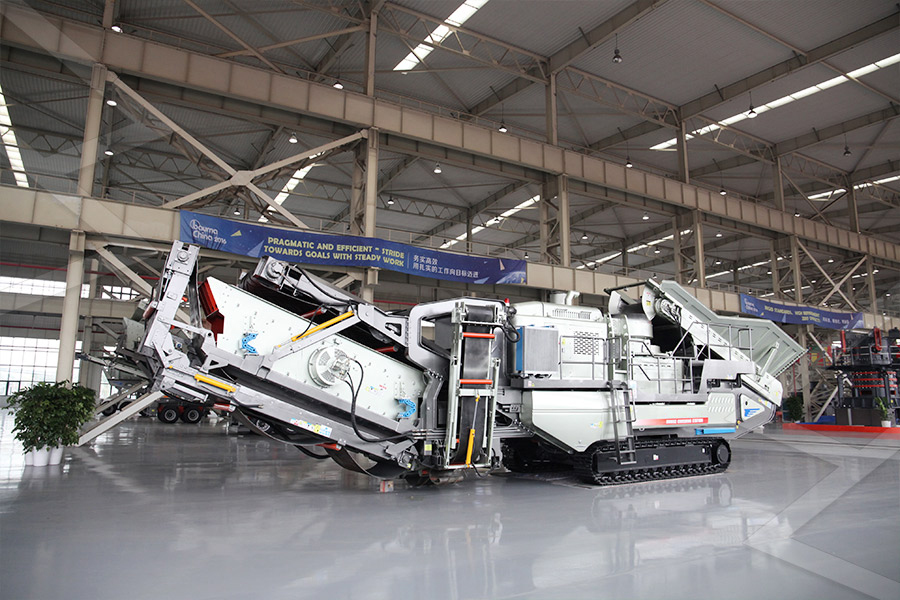
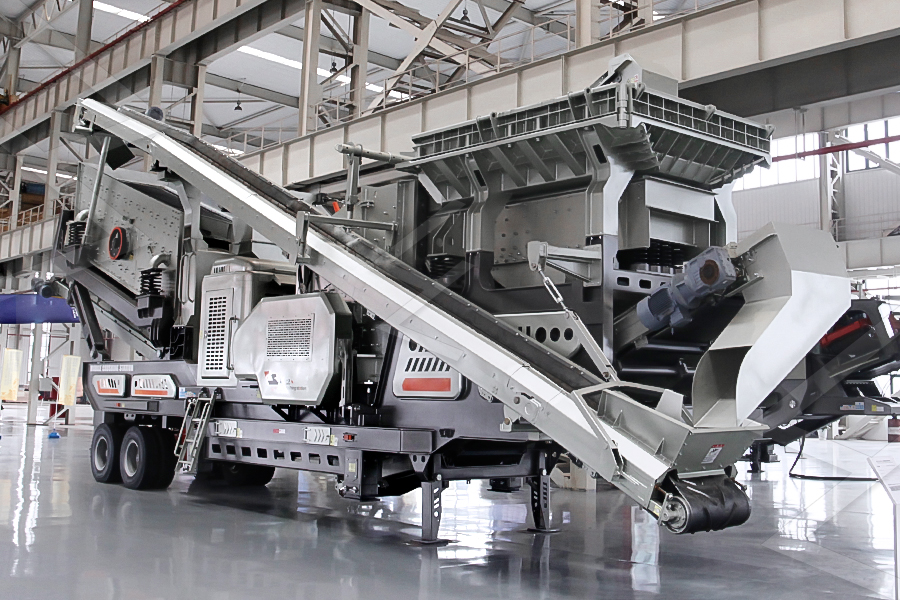
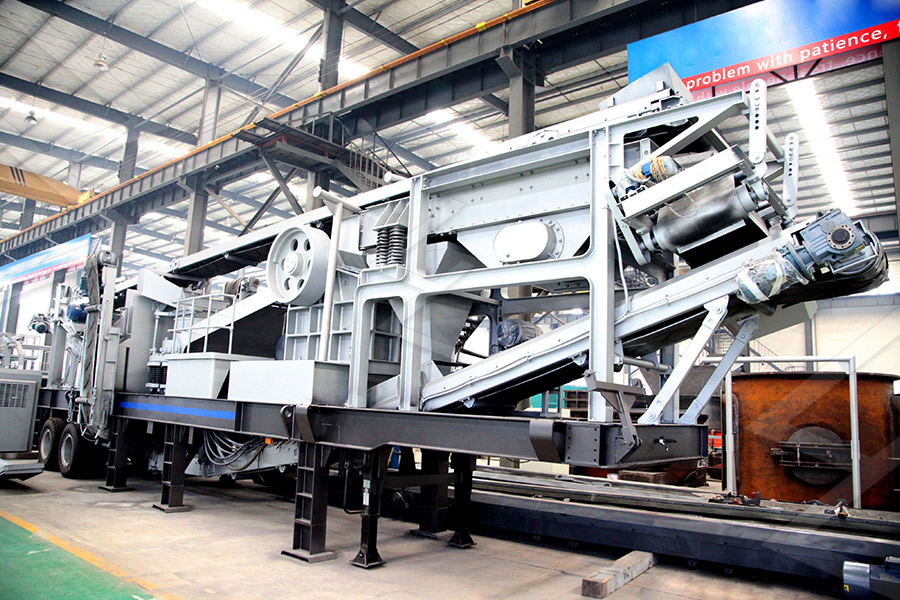
Mobile Crusher