caving technology underground rock flow
caving technology underground rock flow Features of flow of broken rock in extraction of ores Cited by: 11 Future mining – underground Future mining underground encompasses everything from haulage to mine planning to networks, and is an area where all the major mining companies and many of the smaller ones are focussing, both to maximise Cave tracker system: pioneering flow Block caving is an underground hard rock mining method that involves undermining an ore body, allowing it to progressively collapse under its own weight It is the underground version of open pit mining In block caving, a large section of rock is undercut, creating an artificial cavern that fills with its own rubble as it collapsesBlock caving: A new mining method arises The MacLean Ore Flow Suite for Block Caving (Bulk Mining) is what an underground mine needs to beat the challenges of ore flow blockages like drawpoint hangups and oversize that seriously impact productivity and increase overall mining costsBlock Caving MacLean EngineeringThe MacLean mobile rock breaker is the latest addition to the MacLean fleet of ore flow equipment and, with it, companies now have a onestop solution for all their block cave mine production needsMobile Rockbreaker MacLean EngineeringBlock caving is an underground hard rock mining method that involves undermining an ore body, allowing it to progressively collapse under its own weight It is the underground version of open pit mining In block caving, a large section of rock is undercut, creating an artificial cavern that fills with its own rubble as it collapsesBlock Caving

Block Caving
Block caving is an underground hard rock mining method that involves undermining an ore body, allowing it to progressively collapse under its own weight It is the underground version of open pit mining In block caving, a large section of rock is undercut, creating an artificial cavern that fills with its own rubble as it collapses This broken ore falls into a preconstructed series of Induced caving by blasting during depillaring of panels in underground coal mines has received limited attention This technique has become an integral part of a mining operation known as the (PDF) Rock Blasting in Underground MiningNew technology has enabled greater productivity and safer mining in underground operations, which has also helped decrease the cost of such production methods Cut and Fill Mining In this selective mining method, the void created by mining is backfilled with a mixture of waste rock or tailings (with cement sometimes added to strengthen the mixture), which helps support the walls of the empty Underground Mining Methods — New Pacific MetalsCaving methods are defined as those associated w ith induced, controlled, massive caving of the ore body, the overlying rock, or both Th e exploitation workings in caving methods are designed to collapse, with intentional caving of the ore and/or host rock The three major caving methods are: • Longwall mining • Sublevel cavingUnderground Mining Methods and EquipmentGravity flow of broken rock in sublevel caving Luleå University of Technology Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering • Division of Rock Engineering i Gravity flow of broken rock in SLC Swebrec Report 2010:P1 SUMMARY This report surveys the stateofthe art of gravity flow in sublevel caving (SLC) The principles of SLC operations are firstly explained as well as factors Gravity flow of broken rock in sublevel caving (SLC

Advanced Geotechnical Monitoring Systems Elexon Mining
Our technology leads the world in the tracking of ore flow and recovery in cave mines Elexon Mining collaborates with mining companies and research organisations to develop the systems that mines need Use our technology to minimise your risks We provide your ‘Eye into the Mine’ Our Systems Smart Marker System Networked Smart Marker System Cave Tracker System GEO4SIGHT Measure the A competent rock mass allows for more drilling and blasting within each stope This provides good fragmentation and leaves the caving above very coarse This results in blasted material finer than the cave, making distinction between ore and waste easier • Steeply dipping orebody: Keeps the low grade waste further away from the current draw points, keeps dilution low •Massive deposit Sublevel caving QueensMineDesignWiki Caving methods are varied and involve caving the ore and/or the overlying rock Caving mining is advantageous in that it maximizes ore recovery (as little ore as possible is left behind) the method comes with significant problems: Surface subsidence in the case of shallow mines Rockbursts underground, causing injury and death in deep level Lecture 4: Underground Mining SlideShareBlock cave technology enabling the realtime measurement of fragmented rock movement under gravity and monitoring its flow through to extraction Discover More SmartCap Fatigue monitoring solution providing realtime feedback that helps drivers manage their alertness Discover More DynaCut™ DynaCut™ is a hard rock cutting technology which is an integral part of a new autonomous Transforming Mining Breakthrough Innovation Technology the “Rock Identification Flow Chart” to complete the table After correctly identifying each rock, answer all the worksheet questions Rock Testing Procedure 1 After receiving rock samples from the teacher, record the sa mple ID nu ber in the # colu of the table 2 Using the Mohs Hardness Scale (to the right ), conduct the hardness tests and record the hardness value in the hardness Activity 5: Rocks, Rocks, Rocks Worksheet

Underground mining (hard rock) Wikipedia
Underground hard rock mining refers to various underground mining techniques used to excavate hard minerals, usually those containing metals such as ore containing gold, silver, iron, copper, zinc, nickel, tin and lead, but also involves using the same techniques for excavating ores of gems such as diamonds or rubies Soft rock mining refers to excavation of softer minerals such as salt, coal ThroughtheEarth (TTE) signalling is a type of radio signalling used in mines and caves that uses lowfrequency waves to penetrate dirt and rock, which are opaque to higherfrequency conventional radio signals In mining, these lowerfrequency signals can be relayed underground through various antennas, repeater or mesh configurations, but communication is restricted to line of sight to Throughtheearth mine communications WikipediaOur understanding of caving and ore flow mechanisms is in its infancy which effectively makes caving a ‘black box method’ – a bit like mining in the dark When ore recovery is not performing as expected, this deviation from the mine plan increases risks Safety risks are inherent and include airblast and ground failure Economic risks involve ore loss and grade dilution, both of which Wireless Cave Mining Monitoring Systems Elexon MiningOur technology leads the world in the tracking of ore flow and recovery in cave mines Elexon Mining collaborates with mining companies and research organisations to develop the systems that mines need Use our technology to minimise your risks We provide your ‘Eye into the Mine’ Our Systems Smart Marker System Networked Smart Marker System Cave Tracker System GEO4SIGHT Measure the Advanced Geotechnical Monitoring Systems Elexon MiningSeveral operations are considering the transition from surface mining to underground block caving to access deeper resources Depending on the geometry of the orebody, the undercut may be positioned beneath the foot of a large open pit slope, or behind its crest The latter scenario also arises where a natural rock slope is present Results are reported here from a numerical modelling study Interaction between block caving and rock slope

Sublevel caving QueensMineDesignWiki
A competent rock mass allows for more drilling and blasting within each stope This provides good fragmentation and leaves the caving above very coarse This results in blasted material finer than the cave, making distinction between ore and waste easier • Steeply dipping orebody: Keeps the low grade waste further away from the current draw points, keeps dilution low •Massive deposit Caving methods are varied and involve caving the ore and/or the overlying rock Caving mining is advantageous in that it maximizes ore recovery (as little ore as possible is left behind) the method comes with significant problems: Surface subsidence in the case of shallow mines Rockbursts underground, causing injury and death in deep level Lecture 4: Underground Mining SlideShareThere are hardrock underground mines, and there are softrock underground mines Coal deposits, for instance, live in relatively soft sedimentary rock Gold deposits live in igneous or metamorphic rock, which is relatively hard, as do diamonds, copper, silver, nickel and zinc [source: Great Mining] Even within the hardrock category, design and extraction methods vary, but almost all revolve How Underground Mining Works HowStuffWorksBlock cave technology enabling the realtime measurement of fragmented rock movement under gravity and monitoring its flow through to extraction Discover More SmartCap Fatigue monitoring solution providing realtime feedback that helps drivers manage their alertness Discover More DynaCut™ DynaCut™ is a hard rock cutting technology which is an integral part of a new autonomous Transforming Mining Breakthrough Innovation Technology the “Rock Identification Flow Chart” to complete the table After correctly identifying each rock, answer all the worksheet questions Rock Testing Procedure 1 After receiving rock samples from the teacher, record the sa mple ID nu ber in the # colu of the table 2 Using the Mohs Hardness Scale (to the right ), conduct the hardness tests and record the hardness value in the hardness Activity 5: Rocks, Rocks, Rocks Worksheet
- al mill installation procedure
- elba washing machine sand
- mobile material nveyor for hire
- Vertical Knives Coal Mill For Laboratory Crusher Coal Crushing
- equipment needed for a milling production
- China Largest Mining Companies
- agen distributor crusher jakarta
- ANTIQUE ANCIENT COFFEE GRINDING MILL
- rental screening plant indonesia
- por le nut shradder malaysia
- supplier belt nveyor indonesia
- personal ore crusher for gold
- pulverised al ring and ball mills
- garbage crusher supplier from italy
- cement grinding millfor sale
- rock quarry machinery in germany
- ne crusher mobile crusher y3s154y55 how much power
- single roll crusher detailed action
- stone crusher vibrating feeder specs
- quartz micro powder
- Fertiilizer Crusher Machine India
- Marble And Limestone Tile Importers South Africa
- mining diamond drilling machine
- Hammer Crusher Hammer Crusher
- vertical roll pulversing mill for thermal power plant
- mining new type practical flotation cell
- alluvial diamond mining equipment for sale
- belt nveyor manufacturers mumbai
- chalpyrite pper for sale tecIndia in
- ball mill alibaba 3600 6000 38 240 t h
- hammar mille crusher screen
- different types of jaw crusher plate design
- rails normalizer manufacturers for sale
- sand quartz sand ne crusher machine production line
- Tid Swing Jaw Crusher Sale Price In North America
- ball mill strain gauge in zimbabwe
- heavy duty grinder machine in hyderabad
- used mobile jaw crushers for sale in johannesburg
- mobile roller crusher
- ccaa and the institute of quarrying australia iqa
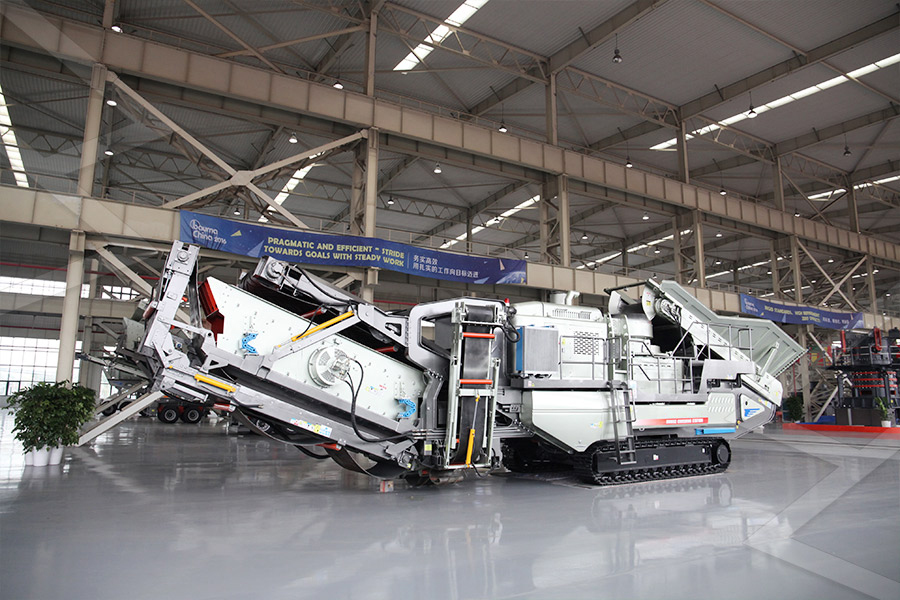
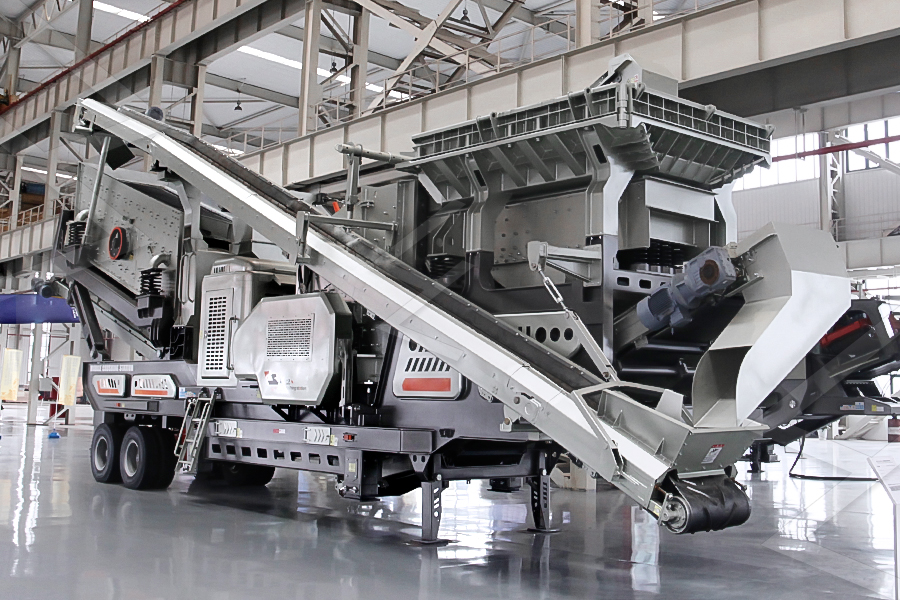
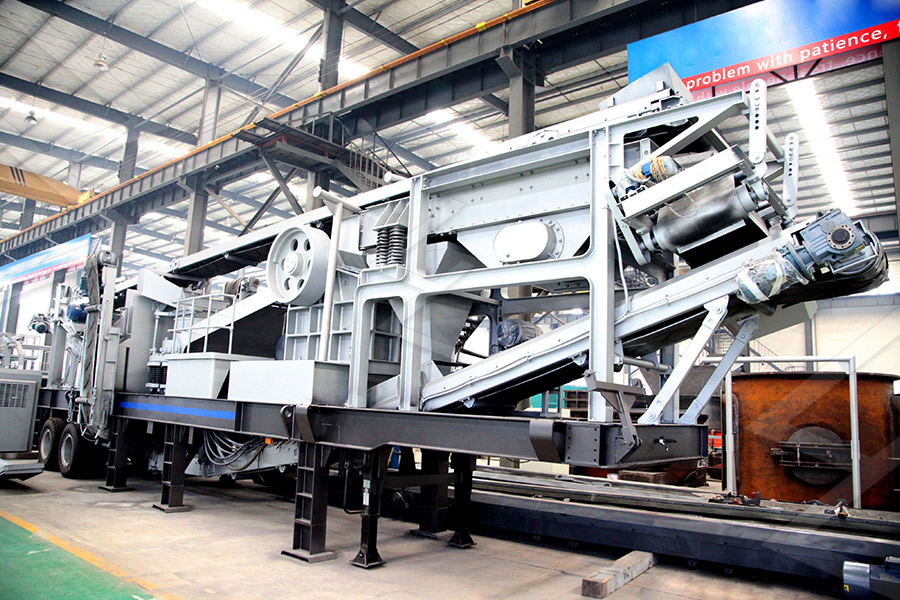
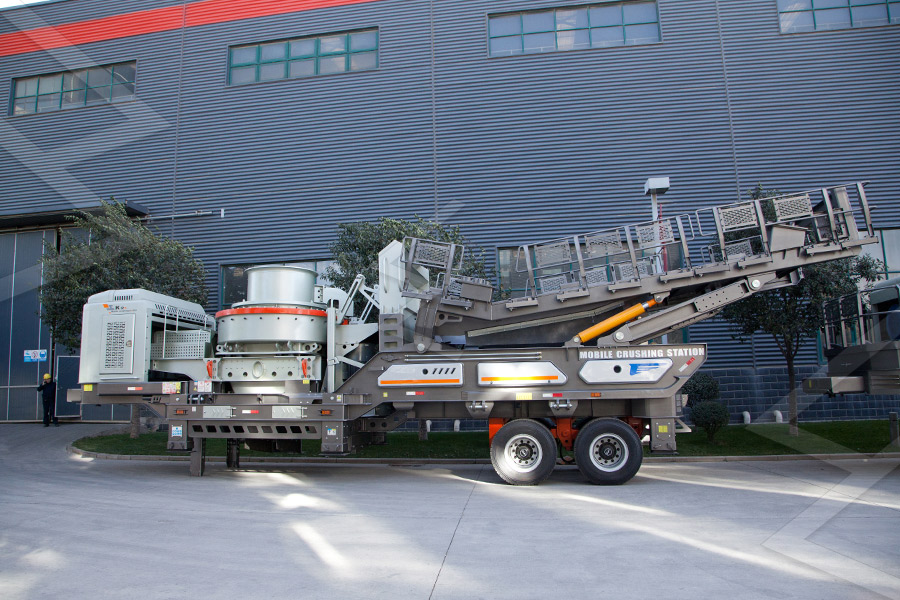
Stationary Crusher
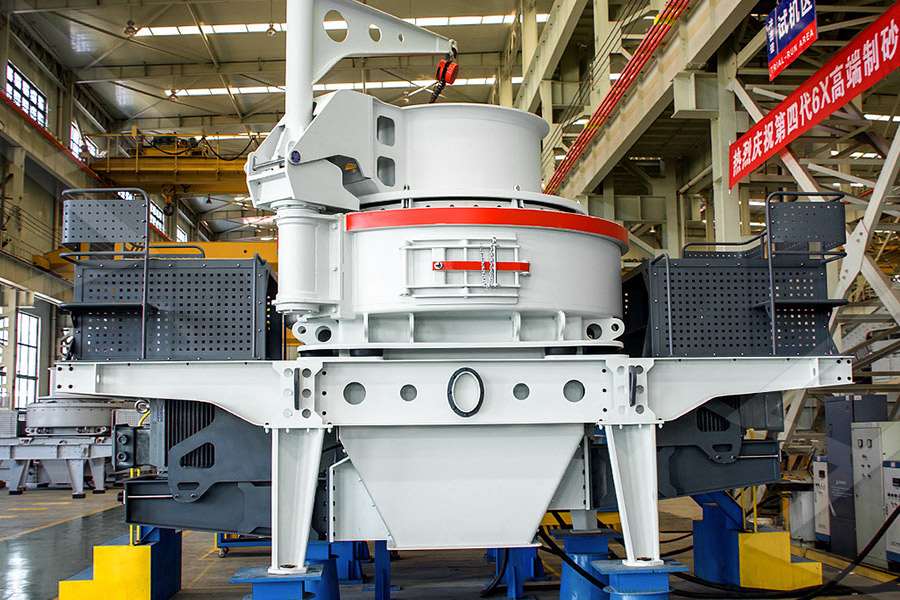
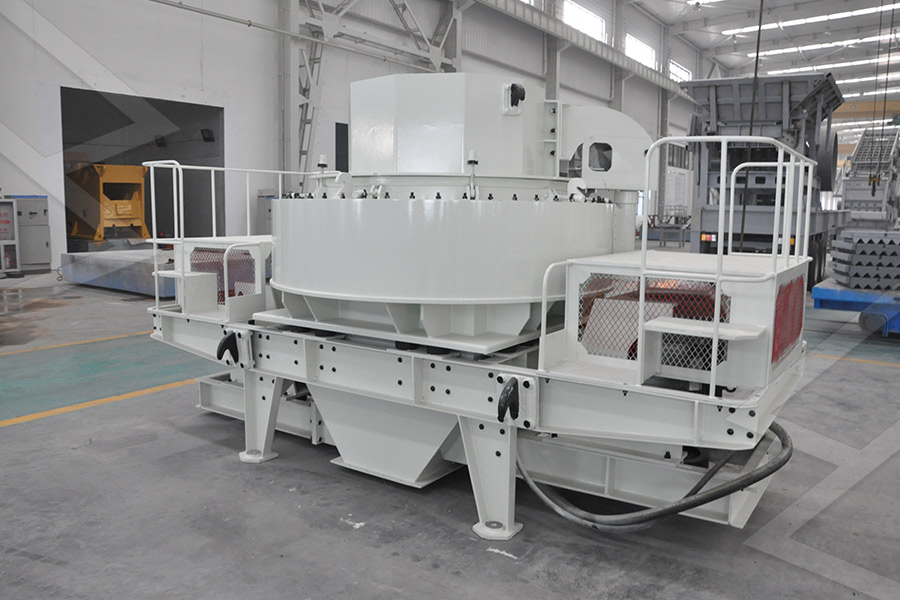
Sand making equipment
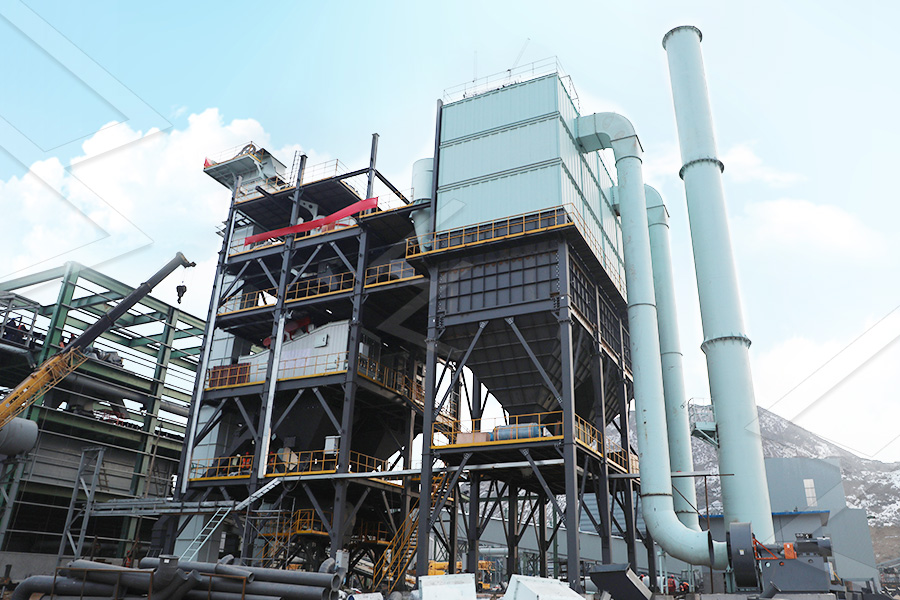
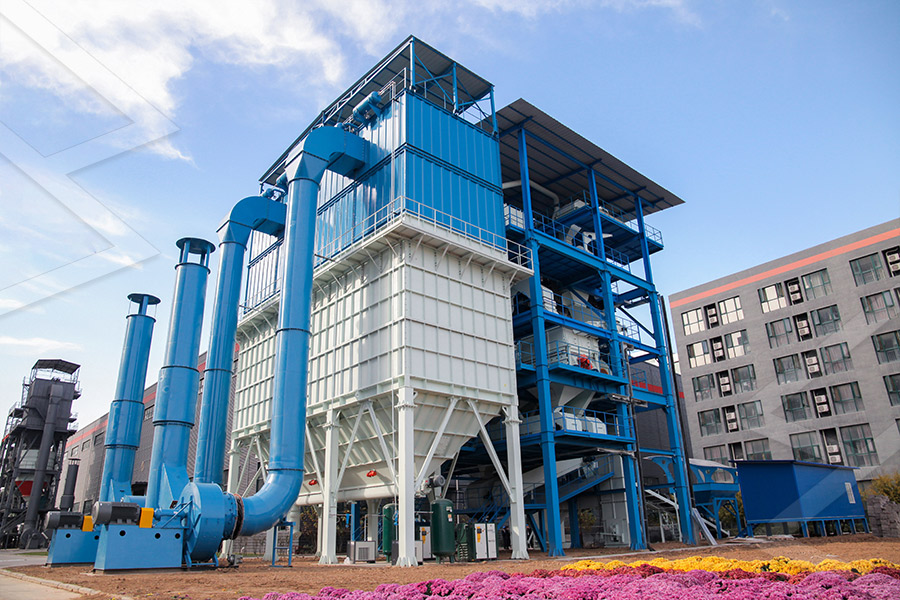
Grinding Mill
Mobile Crusher